Stepper Motor Basics: PM vs VR vs Hybrid
There are three main types of stepper motors available in the market: PM (permanent magnet), VR (variable reluctance), and hybrid. Each has unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Understanding their differences can help you choose the right motor for your needs. Stepper motors operate by rotating in fixed steps, without the need for encoder feedback or complex PID loops. The number of pulses determines the rotation amount, while the frequency controls the speed. Stepper motors offer high repeatability with an accuracy of ±3 arc minutes (±0.05°). They also generate holding torque when powered but stationary, making them ideal for cost-sensitive applications requiring precise positioning and holding force. The design of a stepper motor influences its performance. In this article, we’ll explore the three main types and explain why one might be preferred over another depending on the application. PM (Permanent Magnet) Type A PM stepper motor features a rotor made of two permanent magnets slightly offset from each other. These magnets are axially magnetized, meaning their north and south poles alternate along the same axis as the motor shaft. When current is applied to the stator windings, they become magnetized and align with the opposite poles of the rotor. This interaction causes the rotor to rotate in discrete steps. A common example is the 2-phase claw-type PM motor. The step angle depends on the number of poles and phases. Increasing these values reduces the step angle but may weaken the magnetic force and torque. PM motors are cost-effective and provide higher torque, but their high-speed performance is limited due to losses during rotation. For applications requiring finer resolution, half-stepping or microstepping can be used. However, microstepping requires precise current control, which can increase complexity. Additionally, PM motors typically use constant voltage drivers, which are less efficient than constant current chopper drivers. VR (Variable Reluctance) Type VR stepper motors have Teeth on both the rotor and stator, allowing for a simpler design compared to PM motors. They do not use permanent magnets, so they cannot provide holding or detent torque at rest. Instead, the magnetic flux is concentrated through the teeth, which attract each other when energized. VR motors are known for better high-speed performance than PM motors because they don’t rely on permanent magnets. However, they produce more noise and have less fine torque control since torque is proportional to the square of the current rather than linearly. Their step angle formula involves the number of rotor teeth and phases, and increasing the number of teeth improves resolution but makes manufacturing more complex. VR motors are often used in mid-to-high-speed applications where noise is not a major concern, but they are less common in the market due to their limitations in torque and precision. Hybrid Type Hybrid stepper motors combine the best features of PM and VR designs. They use a permanent magnet rotor and toothed stators to achieve high torque and precision. The combination allows for excellent performance across a wide range of speeds, making them the most popular choice in many industrial applications. Hybrid motors feature a small air gap between the rotor and stator, enabling efficient magnetic flux concentration. They also have a more complex structure, including multiple teeth on both the rotor and stator, which helps reduce step angles and improve resolution. A typical hybrid motor has 50 or 100 teeth, resulting in step angles of 1.8° or 0.9°, respectively. Hybrid motors offer high torque due to the strong permanent magnets, and their performance is more linear compared to VR motors. They are ideal for applications requiring both high torque and high precision, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics. Microstepping can further enhance their resolution, making them versatile for demanding tasks. Summary Hybrid stepper motors are the most popular choice due to their superior performance, even though they come at a higher cost. While PM and VR motors are suitable for specific applications, hybrid motors offer the best overall performance for most uses. Advances in driver technology have made stepper motors smarter and easier to control, expanding their applications further. Adding gearheads or closed-loop feedback can extend their capabilities even more. Working with a manufacturer that provides comprehensive support and training can simplify the integration process. Interested in learning more? Explore our technical articles and white papers on stepper motor fundamentals to deepen your understanding and make informed decisions for your next project. Excavator cylinder: The hydraulic cylinder is a linear actuator whose output force is proportional to the effective area of the piston and the pressure difference between both sides. â€Its function is to convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. The input of the hydraulic cylinder is the flow and pressure of the fluid, and the output is the linear motion speed and force. The piston of the hydraulic cylinder can complete linear reciprocating motion, and the output linear displacement is limited. The hydraulic cylinder is an energy conversion device that converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy for reciprocating linear motion. The hydraulic cylinder is basically composed of a cylinder tube and a cylinder head, a piston and a piston rod, a sealing device, a buffer device and an exhaust device. Welding Cylinder,Cylinder Of Sdlg Loader,Xcmg Loader Steering Cylinder,Wheel Loader Hydraulic Cylinder Jinan Union Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.tfloaderparts.com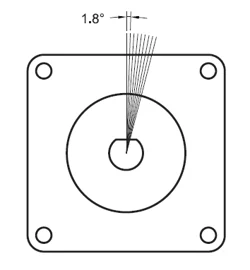
Cylinder maintenance method:
One. The hydraulic oil should be replaced regularly during the use of the cylinder, and the system filter should be cleaned to ensure cleanliness and prolong its service life.
two. Each time the oil cylinder is used, it needs to be fully extended and retracted for 5 strokes and then run with load. Doing so can exhaust the air in the system and preheat the systems, which can effectively avoid the presence of air or water in the system and cause gas explosion (or scorch) in the cylinder body, which will damage the seals and cause leakage in the cylinder. Wait for failure.
three. Control the system temperature. Excessive oil temperature will reduce the service life of the seal. Long-term high oil temperature will cause permanent deformation of the seal or even complete failure.
four. Protect the outer surface of the piston rod to prevent bumps and scratches from damaging the seals. Frequently clean up the mud and sand on the dust ring of the cylinder dynamic seal and the exposed piston rod to prevent difficult-to-clean dirt sticking to the surface of the piston rod Into the inside of the cylinder, damage the piston, cylinder or seal.
Fives. Check the connections of the threads and bolts frequently, and tighten them immediately if they are loose.
six. Frequently lubricate the connecting parts to prevent corrosion or abnormal wear in the absence of oil.
SEM 50F, 650 Welding Cylinder
Liugong loaders ZL50CN, 855N, 856 Welding Cylinder,
SDLG 956L 952H 953 Carbon Fiber Steering Cylinder,
XCMG Steering Cylinder LW500KL ZL50GN,
Komatsu WA380, WA380-3, WA380-5, WA430-5 Steering Cylinder
DEGONG loader Hydraulic System
Foton Lovol Loader Hydraulic Cylinder
Lonking 855N loader Hydraulic Cylinder
XGMA 932 936 956 Loader Hydraulic Cylinder
Changlin Loader Hydraulic Cylinder
Shantui SL50W Custom hydraulic system
And we have more.