
Choosing the right piping material is a crucial decision that depends on various factors, including the operating conditions, chemical exposure, and mechanical requirements. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each material to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Every piping material has its own set of advantages and limitations, and selecting the wrong one can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of the entire system.
To extend the lifespan of piping systems, regular inspections and proper maintenance are essential. This ensures that any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage are identified and addressed before they lead to failures or costly repairs.
Table of contents
- 25 Types of Piping Material Used in Oil and Gas Industry
- Stainless Steel Function in Corrosive Environments
- Pros and Cons of Carbon Steel
- Pros and Cons of Alloy Steel
- Application of HDPE Pipe
- Duplex and Super Duplex Advantages and Disadvantages
- Benefits of Using Nickel Alloy Material in Oil and Gas Applications
- Fiberglass and Polyvinylidene Fluoride Material Uses in Oil and Gas Applications
- Corrosion Agents in Oil & Gas
- Corrosion Threats in Oil & Gas Applications
- Piping Material Inspection Checklist
- Pros and Cons of Copper, Brass, Galvanized Steel, PVC, Aluminum Material
- Mechanical Properties of Pipe Materials
- Metallic Piping Materials Effects of Alloying Elements
- Typical Pipe Material Selection Criteria
- Carbon Steel With Epoxy Coating
- Material Service Checks
- Copper Nickel Advantages
Steel pipes are used by oil and gas industries to transport gas and liquids
In the oil and gas industry, steel pipes are widely used due to their versatility and ability to handle a wide range of fluids and gases under varying conditions. While not all steel pipes offer the same properties, each type is designed for specific applications. Below are some of the most commonly used steel pipe materials in this sector.
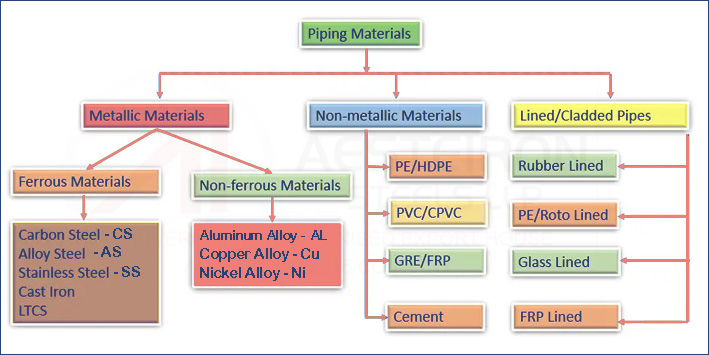
25 Types of Piping Material Used in Oil and Gas Industry
| Material |
Grades |
| Carbon Steel |
|
| Alloy Steel |
|
| Stainless Steel |
|
| Duplex Stainless Steel |
|
| Nickel-Alloy Steel |
|
| Super Duplex Stainless Steel |
|
| Titanium |
|
| Hastelloy |
|
| Monel |
|
| PVC |
– |
| CPVC |
|
| Silicon Bronze |
|
| HDPE |
– |
| PEX |
– |
| Stainless Steel with Internal Lining |
Various linings |
| Fiberglass |
FRP |
| Carbon Steel with CRA Lining |
Various CRA materials |
| High-Performance Alloys |
Various specialty alloys |
| Concrete-Lined Steel Pipe |
– |
| Copper |
– |
| Brass |
|
| Aluminum |
|
| Zirconium |
|
| Alloy 20 |
– |
| Lead |
– |
SS pipes are widely used in petroleum industry due to its corrosion resistance property
Stainless steel pipes are known for their exceptional resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for use in the petroleum industry. These pipes contain at least 10.5% chromium, which reacts with oxygen in the air to form a protective oxide layer that prevents rust and other forms of degradation. This makes stainless steel an excellent choice for environments where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Stainless Steel Function in Corrosive Environments
| Type of Stainless Steel |
Grades |
Corrosion Resistance |
| Austenitic |
304, 304L, 316, 316L, 317, 321, 347 |
High resistance to general corrosion and chloride situations |
| Duplex |
2205 |
Superior tensile strength and stress corrosion breaking resistance |
| Super Duplex |
2507 |
Exceptionally strong and resistant to corrosion |
| Martensitic |
410, 420 |
Greater hardness and less resistance to corrosion |
Most common types of piping material are carbon steel and alloy steel
The following table outlines the pros and cons of carbon steel and alloy steel, helping you make an informed decision based on your application needs.
Pros and Cons of Carbon Steel
| Pros |
Cons |
| Cost-effective |
Susceptible to corrosion |
| Good strength and durability |
Need protective coatings or cathodic protection |
Pros and Cons of Alloy Steel
| Pros |
Cons |
| High strength and toughness |
More expensive |
| Suitable for high-stress applications |
Need careful handling and welding |
| Good resistance to high temp. and pressure |
|
HDPE pipe is widely used to transfer fluids and gases
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes are flexible and durable, often used for transporting fluids and gases. They are manufactured from high-density polyethylene, which provides strong molecular bonding and makes them suitable for high-pressure pipeline applications. HDPE is also cost-effective and resistant to many chemicals, making it ideal for various industrial uses.
HDPE pipes are particularly useful in applications where cost-effectiveness, strength, and durability are required. Below are some of the key areas where HDPE pipes are highly effective.
Application of HDPE Pipe
- Pipeline Transportation
- Chemical Handling
- Underground Installations
- Offshore
- Drilling & Exploration
- Water Injection
- Environmental Protection
- Infrastructure
In the offshore industry mainly duplex and super duplex piping are used
Duplex and super duplex steels are preferred in offshore environments due to their superior strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness. These materials contain higher levels of chromium, molybdenum, and nitrogen, which enhance their performance in harsh conditions.
Duplex and Super Duplex Advantages and Disadvantages
| Material |
Pros |
Cons |
| Duplex |
High Strength |
Lower Corrosion Resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance |
Limited Temp. Range |
| Cost-Effectiveness |
Potential for Sensitization |
| Good Weldability |
Thermal Sensitivity |
| Super Duplex |
Superior Strength |
Expensive |
| Enhanced Corrosion Resistance |
Limited Weldability |
| High Resistance to Erosion and Abrasion |
Thermal Sensitivity |
| Cost Efficiency |
Potential for Sensitization |
Benefits of Using Nickel Alloy Material in Oil and Gas Applications
- Corrosion Resistance
- High-Temperature Performance
- Wear and Erosion Resistance
- Mechanical Properties
- Hydrogen Sulfide Resistance
Fiberglass and Polyvinylidene Fluoride Material Uses in Oil and Gas Application
Fiberglass Application
- Offshore
- Seawater
- Hydrocarbon Transport
- Cooling Water Systems
- Chemical Handling Systems
- Tank Linings
- Ventilation and Drainage Systems
Polyvinylidene Fluoride Application
- Chemical Injection
- Acid and Alkali Transport
- Refining Processes
- Seawater Systems
- Used in high-purity fluid
- Cooling Systems used where chemical resistance is crucial
Corrosion Agents in Oil & Gas
- Carbon Dioxide
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen Sulphide
- Water
- Chlorides
Corrosion Threats in Oil & Gas Applications
- Sweet Corrosion – CO2 Corrosion
- Sour Corrosion – H2S Corrosion
- Corrosion due to Oxygen
- Chlorides and Bicarbonates
- Erosion Corrosion
- Microbiologically
- Corrosion Under Insulation
- External Atmospheric Corrosion
Piping Material Inspection Checklist
- Visual Inspection
- Dimensional Check
- Material Certification
- Weld Inspection
- Corrosion and Coating Inspection
- Pressure Rating and Testing
- Documentation and Compliance
Pros and Cons of Copper, Brass, Galvanized Steel, PVC, Aluminum Material
| Pipe Material |
Pros |
Cons |
| Copper |
- Durable and long-lasting
- Corrosion resistance
- Flexible
- Recyclable
|
- Expensive
- High thermal conductivity
|
| Galvanized Steel |
- Strong and durable
- Corrosion resistant due to zinc coating
- Long service life
|
- Higher cost
- Difficult to handle
- Can rust over time
|
| Brass |
- Corrosion resistant
- Strong and durable
- Easy to machine
|
- Expensive
- Can become brittle over time
|
| PVC |
- Easy to install
- Cost-effective
- Low maintenance
|
- Not suitable for high temperature applications
- Environmental impact of production
|
| Aluminum |
- Naturally corrosion resistant
- Lightweight
- Easy to install
|
- Scratching and denting
- Can be costly
|
Mechanical Properties of Pipe Materials
- Modulus of Elasticity: Stress to strain ratio measured using tension tests
- Plastic range
- Elastic range
- Yield Strength
- Ultimate Tensile Strength
- Hardness: Tested by Brinell or Rockwell
- Ductility
- Fatigue Resistance
- Toughness
Metallic Piping Materials Effects of Alloying Elements
| Alloying Element |
Effect |
| Carbon |
 |
- Increases hardness, wear resistance, and strength
- Reduces ductility
|
| Chromium |
 |
- Enhances oxidation and corrosion resistance, hardness, toughness, and strength
|
| Molybdenum |
 |
- Increases strength and hardness at high temperatures
|
| Manganese |
 |
- Increases strength, wear resistance, toughness, ductility, and hardness
|
| Silicon |
 |
- Increases strength, oxidation resistance, and hardness
|
| Copper |
 |
- Increases strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking
|
| Tungsten |
 |
- Improves hardness, wear resistance, and strength at high temperatures
|
Typical Pipe Material Selection Criteria

Nickel 200/201
- Good mechanical properties
- Excellent corrosive resistance
- Good ductility at low temp
- Excellent weldability
Monel 400/500
- Good resistance to acidic conditions
- Ni-Cu Alloy
- Good ductility at low temp
- UNS 04400 – up to 550°C
- UNS 05500 – up to 650°C
Inconel Selection
| Inconel 600/601 |
Inconel 625 |
Inconel 825 |
Inconel 800 |
Inconel 800H |
| Ni-Cr-Fe |
Ni-Cr-Mo-Fe |
Ni-Cr-Mo-Fe |
Ni-Cr-Fe |
Ni-Cr-Fe |
| Excellent oxidation |
Excellent strength |
High resistance to seawater, phosphoric and sulfuric acid |
– |
– |
| Excellent corrosive resistance |
Good ductility |
Good corrosion resistance |
– |
– |
| Weldability |
Better weldability |
used in condenser and heat exchanger |
– |
– |
Hastelloy Selection
- Suitable for extremely corrosive conditions
- Best for strong acids, seawater, formate acids, and saline solutions
- Good for oxidizing applications
- Corrosion resistant to wet hydrochloride solutions
Titanium – B861 / B862
- About 6% Nitrogen
- Excellent erosion resistance
- High strength
- Good formability, toughness and weldability
- Zero corrosion allowance
Carbon Steel With Epoxy Coating
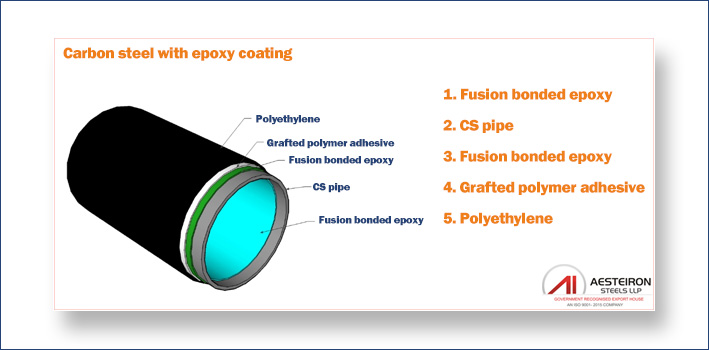
Material Service Checks
| Caustic |
- Need to check NaOH or KOH concentration
- Require CS and PWHT material
|
| Amine |
- Services – MEA, DIPA, DEA, DGA
- Fluid velocity : < 2 m/sec for CS
- SS for high temps and velocity
|
| Oxygen |
- Carbon, stainless and monel material used
- Try to avoid threaded piping
- Cleanliness required
|
| Wet H2S |
- In water : > wt% 50 to 75 ppm
- Hardness : 200 BHN
|
| Ammonia |
- Cryogenic material used for gaseous service
- carbon steel temp. must be > -29°C
|
| Hydrogen |
- Carbon steel used up to 232°C
- SS used up to 330° to 400°C
- Inconel 800 used up to 400°C
|
| Chlorine |
- Carbon steel is used in liquid chlorine
- PWHT is not required
|
| Hydrofluoric Acid |
- Concentration > 1ppm
- hardness up to 200 BHN
|
Copper Nickel Advantages
- Excellent seawater corrosion resistance
- Long service life
- Better hydraulic performance
Lotion Bottle
We are China Lotion Bottle,Airless Lotion Bottle manufacturer supplier & manufacturer, offer low price, high quality control
Lotion bottle is is one type of Cosmetic Bottle,high grade,with Acrylic outer ,PP inner.
The volume has 30ml 50ml 60ml 80ml 100ml 120ml etc.
There are many different kinds can choose,
Use for face cream,eye cream and other cosmetic packaging.
Lotion Bottle,Airless Lotion Bottle,Airless Pump Bottle,Bottles Of Lotion
NINGBO CRETE PLASTIC CO.,LTD , https://www.crete-sprayer.com













